Cloud Cryptography: A Beginner's Guide for Everyday Users
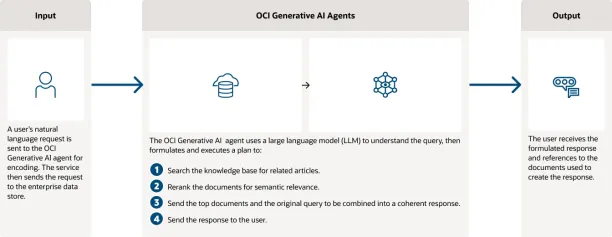
The globalization and technological evolution of the modern age have led humanity to discover cloud computing. However, such convenience brings an important question: How do we ensure that our sensitive data remains secure? The key to this issue can be found in cloud cryptography—an intriguing domain that employs Encryption to protect data when it queries the cloud. Let's break this down in a simple way with a fun conversation between an IT expert and Osinachi, a curious 10-year-old who's just starting to explore the internet. A Fun Chat About Cloud Security Osinachi: Hey! Quick question. All this talk about "the cloud" — like Google, Apple, and Microsoft services — how safe is it? My data's not just floating around in the air. IT Expert: (Laughs) It's not just floating above your head like a raincloud! Think of it as a super-secure vault… but online. Osinachi: Hmm. But can someone hack into it? Like those cool spies in movies? IT Expert: Only if they're a genius with a lot of time and resources. But that's why we use cryptography. Your data is scrambled into a secret code. So even if someone grabs it, they can't understand it. Osinachi: Oh! So it's like sending my data in a locked box? IT Expert: Exactly! And only you have the key. Unless, of course, you make your key something silly like "12345." Osinachi: Ha! I feel called out. IT Expert: (Smiles) We've all been there. I'm just kidding, but cloud providers do take security seriously. They protect your data with Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure connections. Osinachi: So, are you telling me that Apple, Google, and the others are using James Bond-level tech to keep my files safe? IT Expert: Pretty much! And they do it all in the background, so you don't notice. Think of it like having James Bond guarding your data… minus the tuxedo! Osinachi: That's cool. But wait, isn't the cloud like a big public space? Isn't everyone using the same servers? IT Expert: Good question! Think of it like an apartment building. You've got your own locked space, completely separate from everyone else's. Even if someone causes trouble in their apartment, your space stays secure. Osinachi: Got it! So, are there no uninvited guests crashing my data party? IT Expert: Exactly! Your data stays yours. What is Cloud Cryptography? Cloud cryptography uses Encryption to protect data stored or processed in cloud environments. Encryption turns your data into a scrambled code (ciphertext) that can only be read by someone with the correct key to decrypt it. This ensures that even if unauthorized parties intercept the data, they won't be able to make sense of it. Standard Cryptographic Techniques Used in the Cloud Here are four standard encryption techniques you'll find in cloud security: 1. Symmetric Encryption It uses a single key to both encrypt and decrypt data. It's fast and efficient but requires secure sharing of the key. Examples: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Data Encryption Standard (DES). 2. Asymmetric Encryption Involves a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key encrypts the data, but only the private key can decrypt it. Examples: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography). 3. Hashing Converts data into a fixed-length value (a hash) that can't be reversed to its original form. Hashing ensures data integrity by detecting any changes. Commonly used in blockchain, digital signatures, and database indexing. 4. Hybrid Encryption Two types of keys are used for hybrid encryption: asymmetric (public and private) and symmetric (a shared key). It secures online communication. For instance, when you access a secure website, a temporary key is generated through asymmetric encryption that will be used to encrypt your data with symmetric encryption at a higher speed. Consider, for example, encrypted email. A shared key is used to encrypt the message by the sender, and the same key is then secured using the public key of the receiver. The recipient uses their private key to unlock the shared key, allowing them to decipher the message. Benefits of Cloud Cryptography: Let us list some of the important benefits of cloud data encryption using cryptography: ✅ Data Privacy: With Encryption, only authorized users can access sensitive data. ✅ Security-Optimized: Data is secured in its storage and transfer phases (in transit; at rest). ✅ Regulatory Compliance: Enables businesses to comply with data protection regulations by protecting sensitive data. Challenges of Cloud Cryptography: Here we go with the challenges we can face regarding cloud cryptography. But although cloud cryptography is highly secure, it does present some challenges

The globalization and technological evolution of the modern age have led humanity to discover cloud computing. However, such convenience brings an important question: How do we ensure that our sensitive data remains secure? The key to this issue can be found in cloud cryptography—an intriguing domain that employs Encryption to protect data when it queries the cloud.
Let's break this down in a simple way with a fun conversation between an IT expert and Osinachi, a curious 10-year-old who's just starting to explore the internet.
A Fun Chat About Cloud Security
Osinachi: Hey! Quick question. All this talk about "the cloud" — like Google, Apple, and Microsoft services — how safe is it? My data's not just floating around in the air.
IT Expert: (Laughs) It's not just floating above your head like a raincloud! Think of it as a super-secure vault… but online.
Osinachi: Hmm. But can someone hack into it? Like those cool spies in movies?
IT Expert: Only if they're a genius with a lot of time and resources. But that's why we use cryptography. Your data is scrambled into a secret code. So even if someone grabs it, they can't understand it.
Osinachi: Oh! So it's like sending my data in a locked box?
IT Expert: Exactly! And only you have the key. Unless, of course, you make your key something silly like "12345."
Osinachi: Ha! I feel called out.
IT Expert: (Smiles) We've all been there. I'm just kidding, but cloud providers do take security seriously. They protect your data with Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure connections.
Osinachi: So, are you telling me that Apple, Google, and the others are using James Bond-level tech to keep my files safe?
IT Expert: Pretty much! And they do it all in the background, so you don't notice. Think of it like having James Bond guarding your data… minus the tuxedo!
Osinachi: That's cool. But wait, isn't the cloud like a big public space? Isn't everyone using the same servers?
IT Expert: Good question! Think of it like an apartment building. You've got your own locked space, completely separate from everyone else's. Even if someone causes trouble in their apartment, your space stays secure.
Osinachi: Got it! So, are there no uninvited guests crashing my data party?
IT Expert: Exactly! Your data stays yours.
What is Cloud Cryptography?
Cloud cryptography uses Encryption to protect data stored or processed in cloud environments. Encryption turns your data into a scrambled code (ciphertext) that can only be read by someone with the correct key to decrypt it. This ensures that even if unauthorized parties intercept the data, they won't be able to make sense of it.
Standard Cryptographic Techniques Used in the Cloud
Here are four standard encryption techniques you'll find in cloud security:
1. Symmetric Encryption
It uses a single key to both encrypt and decrypt data.
It's fast and efficient but requires secure sharing of the key.
Examples: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Data Encryption Standard (DES).
2. Asymmetric Encryption
Involves a pair of keys: a public key and a private key.
The public key encrypts the data, but only the private key can decrypt it.
Examples: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography).
3. Hashing
Converts data into a fixed-length value (a hash) that can't be reversed to its original form.
Hashing ensures data integrity by detecting any changes.
Commonly used in blockchain, digital signatures, and database indexing.
4. Hybrid Encryption
Two types of keys are used for hybrid encryption: asymmetric (public and private) and symmetric (a shared key). It secures online communication. For instance, when you access a secure website, a temporary key is generated through asymmetric encryption that will be used to encrypt your data with symmetric encryption at a higher speed.
Consider, for example, encrypted email. A shared key is used to encrypt the message by the sender, and the same key is then secured using the public key of the receiver. The recipient uses their private key to unlock the shared key, allowing them to decipher the message.
Benefits of Cloud Cryptography:
Let us list some of the important benefits of cloud data encryption using cryptography:
✅ Data Privacy: With Encryption, only authorized users can access sensitive data.
✅ Security-Optimized: Data is secured in its storage and transfer phases (in transit; at rest).
✅ Regulatory Compliance: Enables businesses to comply with data protection regulations by protecting sensitive data.
Challenges of Cloud Cryptography:
Here we go with the challenges we can face regarding cloud cryptography.
But although cloud cryptography is highly secure, it does present some challenges