Simplifying Hybrid Cloud Connectivity with AWS Transit Gateway
Managing network connectivity across multiple Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and on-premises environments can be a complex and resource-intensive task. From juggling multiple VPN connections to ensuring secure, scalable, and high-performance architecture, the challenges grow with the size of your network. AWS Transit Gateway simplifies this process by serving as a centralized hub, enabling seamless, reliable, and scalable connectivity for your cloud-driven operations. In this post, we’ll explore the fundamentals of AWS Transit Gateway, its standout features, practical use cases, and proven best practices to optimize hybrid cloud networks. What is AWS Transit Gateway? AWS Transit Gateway is a managed network service designed to centralize connectivity between Amazon VPCs, on-premises data centers, and other AWS accounts. By removing the complexity of peering relationships and reducing the need for multiple VPN connections, it simplifies network management and enhances operational efficiency. Image Source: AWS Documentation (Source) Key Features of AWS Transit Gateway Centralized Connectivity: Connect up to 5,000 VPCs and VPN connections through a single gateway. Scalability: Seamlessly scale your network as your business grows. Security: Encrypt data in transit and enforce network security policies. High Availability: Built-in redundancy and fault tolerance ensure minimal downtime. Cost Efficiency: Simplifies network architecture, reducing management overhead. Use Cases and Recommendations 1. For Production-Critical or Latency-Sensitive Applications Direct Connect: Utilize AWS Direct Connect, a dedicated network connection between your on-premises data center and AWS, for high bandwidth, consistent performance, and low latency. VPN Backup: Enhance resilience by configuring a Site-to-Site VPN as a backup. This ensures connectivity during any Direct Connect outages, maintaining operational continuity. 2. For Less Demanding Workloads VPN-Only: Opt for a VPN connection when workloads don’t require high performance or low latency. VPN is ideal for development, testing, or non-critical applications. 3. Hybrid Environments Multi-Account Setup: Consolidate networking across multiple AWS accounts using AWS Transit Gateway and AWS Organizations for centralized management and billing. Disaster Recovery and Compliance: Use Transit Gateway for cross-region replication and compliance-sensitive workloads requiring secure data transfer. Best Practices for Using AWS Transit Gateway 1. Monitor and Optimize: Leverage AWS Transit Gateway Network Manager and Amazon CloudWatch to track performance and diagnose bottlenecks. Regularly review routing configurations to adapt to changing traffic patterns. 2. Strengthen Security: Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and AWS Firewall Manager for centralized security control. Encrypt all data in transit and enforce strict security policies across the network. 3. Manage Costs Effectively: Monitor Transit Gateway expenses using AWS Cost Explorer. Consolidate traffic flows to maximize cost-efficiency. 4. Plan IP Addressing Carefully: Avoid routing conflicts by ensuring that each VPC has a unique IP address range. Conclusion AWS Transit Gateway is a game-changer for simplifying connectivity across multiple VPCs and on-premises environments. Whether you need the low-latency reliability of Direct Connect, the cost-efficiency of VPN, or a combination of both for resilience, Transit Gateway provides the flexibility to optimize your hybrid cloud network. Explore AWS Transit Gateway today to unlock secure, scalable, and cost-effective network connectivity that grows with your business.
Managing network connectivity across multiple Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and on-premises environments can be a complex and resource-intensive task. From juggling multiple VPN connections to ensuring secure, scalable, and high-performance architecture, the challenges grow with the size of your network. AWS Transit Gateway simplifies this process by serving as a centralized hub, enabling seamless, reliable, and scalable connectivity for your cloud-driven operations.
In this post, we’ll explore the fundamentals of AWS Transit Gateway, its standout features, practical use cases, and proven best practices to optimize hybrid cloud networks.
What is AWS Transit Gateway?
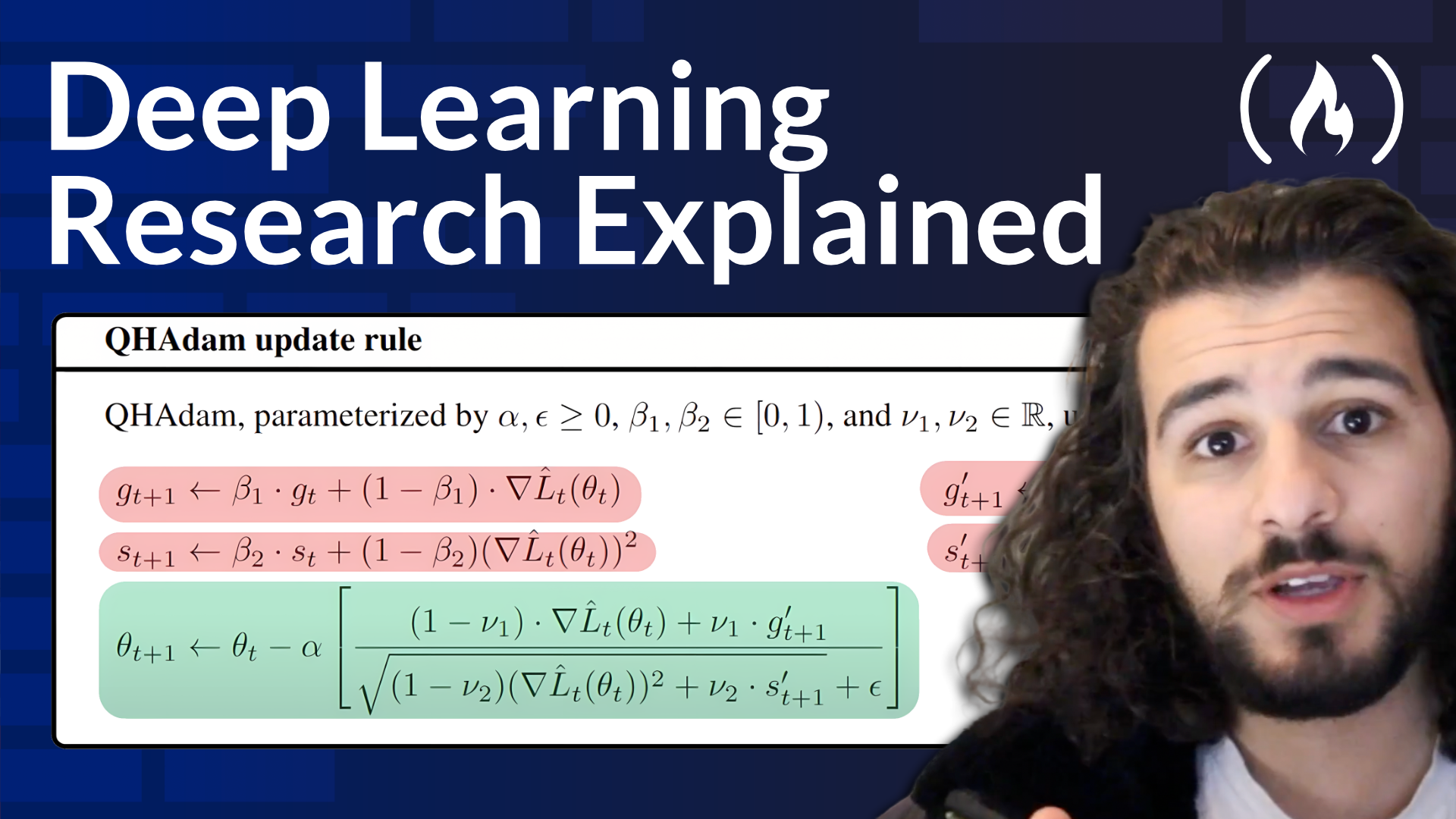
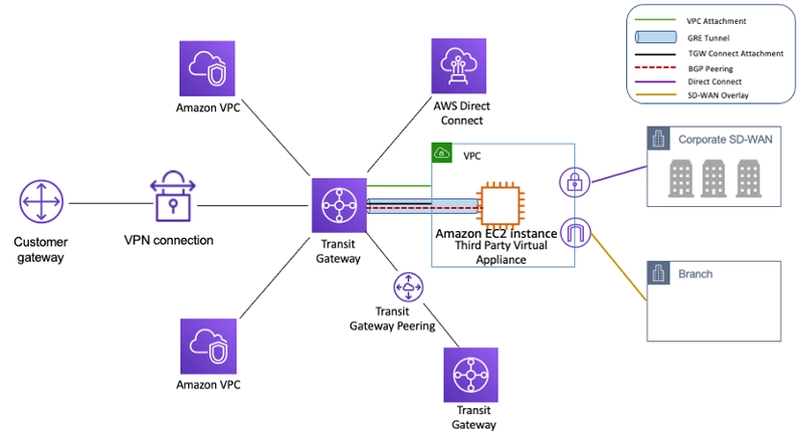
AWS Transit Gateway is a managed network service designed to centralize connectivity between Amazon VPCs, on-premises data centers, and other AWS accounts. By removing the complexity of peering relationships and reducing the need for multiple VPN connections, it simplifies network management and enhances operational efficiency.
 Image Source: AWS Documentation (Source)
Image Source: AWS Documentation (Source)
Key Features of AWS Transit Gateway
- Centralized Connectivity: Connect up to 5,000 VPCs and VPN connections through a single gateway.
- Scalability: Seamlessly scale your network as your business grows.
- Security: Encrypt data in transit and enforce network security policies.
- High Availability: Built-in redundancy and fault tolerance ensure minimal downtime.
- Cost Efficiency: Simplifies network architecture, reducing management overhead.
Use Cases and Recommendations
1. For Production-Critical or Latency-Sensitive Applications
- Direct Connect: Utilize AWS Direct Connect, a dedicated network connection between your on-premises data center and AWS, for high bandwidth, consistent performance, and low latency.
- VPN Backup: Enhance resilience by configuring a Site-to-Site VPN as a backup. This ensures connectivity during any Direct Connect outages, maintaining operational continuity.
2. For Less Demanding Workloads
- VPN-Only: Opt for a VPN connection when workloads don’t require high performance or low latency. VPN is ideal for development, testing, or non-critical applications.
3. Hybrid Environments
- Multi-Account Setup: Consolidate networking across multiple AWS accounts using AWS Transit Gateway and AWS Organizations for centralized management and billing.
- Disaster Recovery and Compliance: Use Transit Gateway for cross-region replication and compliance-sensitive workloads requiring secure data transfer.
Best Practices for Using AWS Transit Gateway
1. Monitor and Optimize:
- Leverage AWS Transit Gateway Network Manager and Amazon CloudWatch to track performance and diagnose bottlenecks.
- Regularly review routing configurations to adapt to changing traffic patterns.
2. Strengthen Security:
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and AWS Firewall Manager for centralized security control.
- Encrypt all data in transit and enforce strict security policies across the network.
3. Manage Costs Effectively:
- Monitor Transit Gateway expenses using AWS Cost Explorer.
- Consolidate traffic flows to maximize cost-efficiency.
4. Plan IP Addressing Carefully:
- Avoid routing conflicts by ensuring that each VPC has a unique IP address range.
Conclusion
AWS Transit Gateway is a game-changer for simplifying connectivity across multiple VPCs and on-premises environments. Whether you need the low-latency reliability of Direct Connect, the cost-efficiency of VPN, or a combination of both for resilience, Transit Gateway provides the flexibility to optimize your hybrid cloud network.
Explore AWS Transit Gateway today to unlock secure, scalable, and cost-effective network connectivity that grows with your business.